Operation Polo
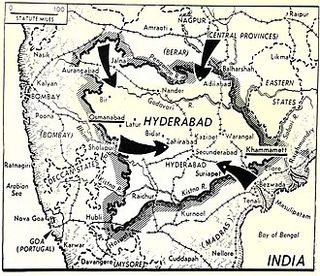
Hyderabad Map before Operation Polo
| Date of Victory | 18th September 1948 |
| Date of Launch | 13th September 1948 |
| Location of event | Hyderabad |
| Type of event | Military Operation |
| Result | Indian Victory |
Operation Polo was a 'Police action' launched on 13th September 1948 against the Nizam Ruled princely state of Hyderabad. After India gained Independence, all princely states were given oppertunity to either join India or Pakistan. If any state wanted to remain independent, it could make a seperate nation. Hyderabad wanted to be a seperate nation and hence declared itself as a Independent nation. Hyderabad being landlocked centrally in India could be future problem for which Sardar Patel held talks with Hyderabad. As the talks didn't not show positive results and the Razakars, militia in Hyderabad turned out to kill and loot the majority Hindu population, India was forced to launch 'Operation Polo' to save people of Hyderabad and annex Hyderabad into Union Of India.
The operation was termed as a police action but was a military operation led by Indian Armed Forces which finished as One United India with victory over Hyderabad on 18th September 1948.
Background
The background is set to 1947 when the Nizam of Hyderabad, Osman Ali Khan Asaf Jah VII decided that the Princely State of Hyderabad will not join India nor Pakistan after Partition. The decision of the Nizam was supported by Pakistan. Being cautious of an opposing independent state in the middle of India, Sardar Patel, the then Deputy Prime Minister, made a decision to annex the state of Hyderabad to India and sent the Indian Army to Hyderabad for the same.[ref]
After Hyderabad's decleration of forming a new nation, Sardar Patel held talks with Hyderabad administration all of which failed. India tried to pressurize Hyderabad but Hyderabad tried to gather attention Pakistan and United Nations to the issue. After getting no proper help due to Indian Diplomacy, they turned harsh over the majority Hindu population. India and Pakistan were divided over Hindu-Muslim issue, turning harsh on Hindus could ressurize India was what they assumed but results turned out to be very different.
The state was also busy arming itself and was receiving arms from Pakistan and the Portuguese administration in Goa.[ref] Razakars, muslim militia of Hyderabad along with Hyderabad forces went into Hindu villages and looted, murdered and raped Hindus. Many villages were burnt and it was the right time for India to act.
Indian Action
As a first step, the Central Government came up with the Standstill Agreement, in November, 1947, which only sought an assurance, that Hyderabad would not accede to Pakistan, and would remain in India. In accordance with the Standstill Agreement, K.M. Munshi was appointed as the Indian Government's envoy and Agent General to Hyderabad. ]
Munshi was mistreated by the Nizam's Government. He was not even given proper accommodation. The Razakars were a private army maintained by the Nizam of Hyderabad. This army started harassing and looting the general public. Against such a background, the Indian Home Minister Sardar Patel decided to annex Hyderabad.
To put an end to all this, the Government under the leadership of Sardar Vallabhai Patel(the then Home Minister of India) and the military leadership of Major General Joyanto Nath Chaudhuri (later Army General), the Government of India managed to free Hyderabad from the control of the Razakars.[ref]
Result
The military action started on 13th September and came to an end on 18th September 1948. The state was surrendered by the Nizam at 4 PM on 18th September 1948. With the surrender, the reign of the Nizams of Hyderabad came to an end.
The Marathi-speaking parts of the erstwhile state were joined with Maharashtra, the Kannada-speaking parts were joined with Karnataka while the Telugu-speaking parts were joined with the Telugu-speaking territories of the Madras Presidency. Major General Joyanto Nath Chaudhuri established a military government in the state until it was replaced by a civil government in 1949 headed by M.K. Vellodi, an ICS officer.[ref]
This war which lasted five days resulted in loss of life and casualties and it is estimated that 32 were killed and 97 injured on the Indian side and 490 killed and 122 wounded on the Hyderabadi side.
The casualities of civilians in riots during this operation still is not confirmed.
